App tracking transparency is a significant development impacting how apps collect and use user data. This guide explores the nuances of this new framework, covering user rights, developer responsibilities, and the evolving landscape of mobile app development. Understanding the intricacies of App tracking transparency is crucial for both users and developers to navigate the changing privacy landscape.
This new framework necessitates a shift in how apps operate, requiring a nuanced understanding of user data collection practices and the rights afforded to users. This guide aims to provide a thorough explanation of App tracking transparency, encompassing user impact, developer considerations, and the wider implications for the mobile app ecosystem.
Introduction to App Tracking Transparency
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) is a significant update to how mobile apps interact with user data, particularly concerning tracking and advertising. It aims to provide users with greater control over their privacy when using apps on their mobile devices. This shift reflects a growing awareness of user privacy concerns and a desire to empower users with choices regarding data collection.The core principle behind ATT is to ensure users are explicitly informed about and consent to tracking practices.
This transparency fosters a more equitable relationship between users and the apps they utilize, shifting the focus from passive data collection to active user participation in the data collection process. The fundamental concept is to put the user in charge of their personal information.
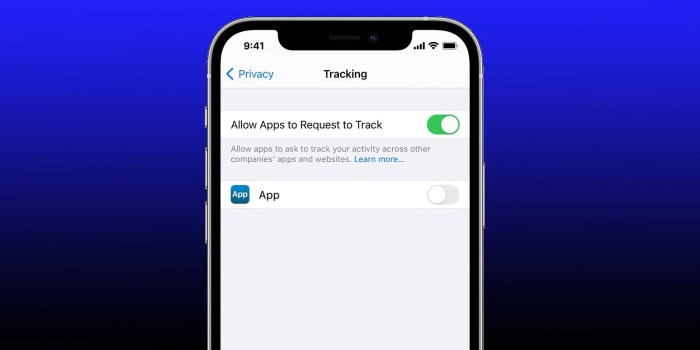
Different Ways Apps Can Request User Permission for Tracking
To comply with ATT, apps must present a clear and concise explanation of how their tracking mechanisms work and how user data will be used. Users are then presented with a choice – to allow or deny tracking. This process typically involves a pop-up or a notification, providing the user with details about the tracking practices.
- App Tracking Request: The app clearly informs the user of its tracking practices and requests permission to track. This is usually presented as a clear prompt within the app itself.
- Transparency and Choice: The app must offer an explanation about the nature of tracking, including how the data will be used, what data will be collected, and to whom it might be shared. Users are presented with an explicit choice to allow or deny tracking.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks for Users and Developers
ATT has the potential to significantly impact both users and developers.
User Benefits
- Increased Privacy Control: Users have the power to choose whether or not their data is tracked, giving them more agency over their personal information.
- Enhanced Transparency: Users can understand how their data is being used by apps, promoting a more informed decision-making process regarding app usage.
- Data Security: Users can actively decide what data is collected and used, thus potentially reducing the risk of misuse or unauthorized access to their information.
Developer Drawbacks
- Reduced Data Collection: Developers may find it harder to gather data for advertising and analytics, potentially impacting their ability to personalize user experiences and develop targeted advertising strategies. This can be a significant challenge for developers reliant on data-driven approaches.
- Potential for Revenue Reduction: Developers who rely on targeted advertising for revenue generation may experience a decrease in income if users choose not to allow tracking.
- Implementation Costs: Implementing ATT compliance mechanisms can introduce additional costs and complexity for developers, particularly for smaller businesses with limited resources.
Developer Benefits
- Improved User Trust: By actively engaging users and being transparent about data collection practices, developers can cultivate a more positive user experience and relationship.
- Focus on Value-Added Services: Developers can focus on offering superior features and functionalities that do not rely on extensive tracking. This fosters user loyalty and retention.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations: ATT can position developers to proactively address privacy regulations and potentially enhance their brand image as being user-centric.
User Impact of ATT
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has significantly altered how users interact with mobile apps, impacting both privacy choices and the user experience. This shift necessitates a careful understanding of how ATT affects user behavior and app design. The fundamental principle is to empower users with control over their data.The implementation of ATT requires developers to transparently inform users about the app’s data collection practices and obtain explicit permission before tracking.
This approach aims to respect user privacy while enabling app functionality. This shift in responsibility has introduced new complexities in the app development landscape, forcing a reevaluation of existing strategies.
User Privacy Choices
Users now have a clear and direct influence over how their data is collected and used by apps. The decision-making process is straightforward: users are presented with a choice to allow or deny tracking. This control allows users to make informed decisions about their data, aligning with evolving privacy expectations.
Impact on User Experience
The implementation of ATT has introduced noticeable changes in the user experience. Some apps may experience reduced functionality, as tracking plays a crucial role in certain features like targeted advertising and personalized content recommendations. This is particularly noticeable in apps relying heavily on user data analysis for personalized features.
Comparison of App Usage with and without Tracking Permissions
The experience of using apps with and without tracking permissions is distinct. Apps that have received permission to track can often deliver more tailored and relevant experiences, potentially improving engagement and utility. Conversely, apps that have not received permission may not be able to offer personalized recommendations or targeted advertisements, potentially impacting user engagement. Examples include recommendation engines, personalized news feeds, and tailored advertisements.
User Control over Data Collection Practices
ATT grants users substantial control over their data. Users are empowered to actively manage the extent to which their data is collected and used. This is a critical aspect of user privacy and allows individuals to align their digital experience with their values and preferences.
User Interface Design Considerations for ATT Compliance
Developers need to design user interfaces that clearly and concisely communicate data collection practices. This includes presenting users with clear and understandable prompts regarding data tracking, allowing users to make informed choices. For example, apps should use clear language in their prompts, avoid overly technical terms, and visually distinguish between the options to allow or deny tracking. A clear and concise explanation of how the app utilizes user data is critical.
A simple, easily accessible ‘privacy policy’ link is also important. A well-designed interface ensures the user understands the implications of their choices.
Developer Considerations for ATT
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has significantly altered the mobile app landscape, demanding developers to adapt their strategies and approaches. This shift requires careful consideration of user privacy, monetization models, and app functionality to ensure a positive user experience and maintain a competitive edge.
App tracking transparency is definitely a key issue, and its evolution will likely be heavily influenced by tech predictions for the next decade. Tech predictions for the next decade suggest a potential shift towards greater user control over data collection. This, in turn, could significantly impact how app developers operate and the overall user experience in the years to come.
Challenges in Implementing ATT
Developers face several challenges in adapting to ATT. A primary hurdle is the need to fundamentally alter data collection practices. Previously common methods of tracking user behavior, often relying on third-party services, are now significantly restricted. This necessitates the development of new methods to understand user engagement and preferences, which can be resource-intensive. Additionally, the complex implementation process, involving updates to existing codebases and new consent mechanisms, presents logistical and technical obstacles.
Strategies for ATT Compliance
Several strategies are available to developers for compliant implementation of ATT. One key approach involves employing alternative data collection methods, such as first-party data. This strategy focuses on direct interactions with users, such as surveys, in-app feedback, and detailed usage analytics. Another strategy focuses on providing valuable, personalized experiences without relying on third-party tracking. This might involve developing personalized content recommendations based on user profiles or in-app interactions.
Furthermore, using a variety of attribution methods, like those provided by app stores, can supplement the lost data from tracking.
Alternative Monetization Strategies
In the absence of third-party tracking, developers need to explore alternative monetization strategies. One effective method is to prioritize in-app purchases and subscriptions. This directly connects user engagement with revenue generation, enabling predictable income streams. Another avenue is to develop freemium models that offer core app functionality for free and premium features for a price. This strategy can appeal to a wider user base while still generating revenue.
Offering premium features based on user engagement or usage can also be a sustainable alternative.
Impact on App Functionality
ATT can affect app functionality in various ways. Apps may experience reduced personalization features if they rely heavily on third-party tracking. However, developers can adapt by utilizing first-party data to provide relevant content and tailored experiences. Reduced ad targeting capabilities may also necessitate a shift towards other monetization strategies. This adaptation might involve focusing on alternative revenue streams, such as subscriptions and in-app purchases.
Obtaining User Consent for Tracking
Obtaining user consent for tracking must be transparent and user-friendly. Developers should provide clear explanations of how the app collects and uses data. Explicitly stating the purpose of data collection and the potential benefits of enabling tracking is crucial. A simple, concise explanation of the privacy policy is vital, alongside a user-friendly consent mechanism. Providing multiple options for granting or denying consent, such as opt-in/opt-out features, should be considered.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) is deeply intertwined with the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations. Understanding the legal frameworks underpinning ATT is crucial for developers to navigate the complexities of user data collection and usage. This section details the legal considerations surrounding ATT, focusing on relevant regulations, potential penalties for non-compliance, and the broader context of data privacy evolution.The legal framework surrounding app tracking is not static.
Laws governing data privacy have become increasingly stringent worldwide, requiring developers to adapt their practices to meet evolving regulatory demands. The impact of these regulations is significant, influencing not only the technical implementation of ATT but also the overall ethical considerations surrounding user data.
Legal Frameworks Related to App Tracking Transparency
Data privacy laws are multifaceted, often encompassing user consent, data collection limitations, and the right to be forgotten. These frameworks, while varying in their specifics, generally emphasize user control over their data. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal ramifications.
Relevant Regulations and Guidelines for App Developers
Numerous regulations and guidelines influence app development practices related to data privacy. These regulations often mandate transparency, consent mechanisms, and user data handling procedures. Developers must meticulously review these regulations to ensure alignment with their app operations.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States is a significant example. It grants California residents specific rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know what data is collected, the right to delete data, and the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information. Developers operating in California must adhere to these provisions, which directly impact how they collect and use user data within their applications.
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe is another crucial example. It emphasizes user rights, including the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data. Developers handling data of EU residents must comply with GDPR’s stringent requirements regarding data processing and user consent. This includes transparent data collection practices, providing users with clear opt-out options, and meticulously documenting data usage.
- Many other regions, such as Brazil with the LGPD, and countries within the EU, have their own regulations that may affect the implementation and compliance of ATT features. This diverse landscape necessitates a global perspective and thorough understanding of the applicable regulations for each jurisdiction in which an app operates.
Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance with ATT
Non-compliance with ATT regulations can lead to severe penalties, ranging from financial fines to legal repercussions. The specific penalties vary based on the violated regulations and the jurisdiction.
- Enforcement mechanisms vary widely. Some regions may impose substantial financial penalties for violations, while others may focus on regulatory orders or cease-and-desist letters. The severity of the penalties can be significant, potentially impacting the financial viability of an app company.
- Examples of potential penalties include substantial fines, court orders mandating changes to data practices, and injunctions prohibiting specific data collection or usage activities. Understanding the potential ramifications is essential for proactively ensuring compliance.
Evolution of Data Privacy Laws and How They Affect ATT
Data privacy laws have evolved significantly in recent years. The growing concern about data security and the increasing interconnectedness of digital platforms have driven the development of more comprehensive and robust regulations.
- Early data privacy laws focused primarily on individual rights. However, contemporary regulations emphasize not only user rights but also the responsibility of data controllers and processors. ATT is an example of how these evolving laws are demanding greater transparency and user control over data usage within applications.
- The emergence of new technologies, such as big data analytics and targeted advertising, has led to the creation of specific regulations designed to address the unique challenges associated with these technologies. This evolution directly influences the implementation and interpretation of ATT, highlighting the importance of staying informed about ongoing developments in data privacy legislation.
Comparison and Contrast of Data Privacy Laws Across Different Regions
Data privacy laws vary significantly across different regions. This diversity necessitates a nuanced understanding of the specific requirements in each jurisdiction where an app operates. The differences in scope, enforcement mechanisms, and specific provisions require careful consideration for app developers.
| Region | Key Data Privacy Law | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Europe (GDPR) | General Data Protection Regulation | Focus on user rights, strong enforcement mechanisms, and comprehensive data protection principles. |
| United States (CCPA) | California Consumer Privacy Act | State-level regulation emphasizing consumer rights, with potential for broader adoption. |
| Brazil (LGPD) | General Data Protection Law | Focus on data protection and user rights, mirroring the GDPR’s structure. |
Technical Implementation of ATT
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) introduces a significant shift in how mobile apps interact with user data regarding tracking. Understanding the technical intricacies of ATT is crucial for developers to ensure compliance and maintain a positive user experience. This section delves into the technical implementation aspects, encompassing the flow, requirements, and user response handling.
Overview of Technical Aspects
The technical implementation of ATT revolves around a permission request mechanism integrated into the operating system (iOS). This system prompts users to consent to app tracking. This approach shifts the control of data collection from the app developers to the end-user, fostering a more privacy-conscious mobile ecosystem. The core mechanism is designed to provide a clear and consistent way for users to manage their tracking preferences across various apps.
Permission Request Flow
The following steps Artikel the typical flow for implementing ATT permission requests:
- The app requests permission to track the user. This request is initiated by the app through a standard API call within the iOS framework.
- The iOS operating system presents a dialog box to the user, clearly outlining the app’s purpose for tracking. This dialog includes details about how the data will be used and the potential implications.
- The user responds to the request by either granting or denying permission. This response is conveyed back to the app.
- The app processes the user’s response and adjusts its tracking activities accordingly.
Technical Requirements for Compliance
Apps must adhere to specific technical requirements to comply with ATT. These requirements focus on transparency and user control.
- Implement the appropriate API calls to request tracking permissions. This includes using the `ATT` API provided by the iOS framework. Correct usage of this API is essential for a smooth user experience and proper implementation.
- Ensure the permission request dialog is clear and concise, outlining the app’s intended use of tracking data. Providing comprehensive information about the purpose and scope of tracking is crucial to transparency and user autonomy.
- Develop a robust mechanism for handling both affirmative and negative user responses. The app must gracefully adjust its behavior based on the user’s choice, ensuring a smooth transition for the user.
- Implement tracking mechanisms that are consistent with the user’s consent. The app should stop tracking if the user denies permission.
Permission Request Dialogs
Different permission request dialogs can be presented to the user, depending on the context and the specific tracking mechanisms employed.
| Dialog Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard Tracking Permission | The most common type, requesting general permission to track user activity. |
| Identifier for Advertisers (IDFA) Permission | Specifically requests permission to access and use the IDFA for advertising purposes. A clear explanation of how the IDFA will be utilized is crucial. |
| Other Tracking Mechanisms | Permissions might be required for various other tracking mechanisms used by the app. These mechanisms should be clearly described in the permission request dialog. |
Handling User Responses
The app must handle user responses to tracking permission requests effectively.
- Granting Permission: The app can proceed with its tracking activities as per the user’s consent. It’s crucial to maintain the user’s privacy by adhering to the defined scope of the permission.
- Denying Permission: The app must cease tracking activities. This may require adjustments to the app’s functionality to avoid unintentional tracking, and potentially alter the user experience. The app should communicate clearly with the user regarding the implications of denying permission, e.g., “Some features might not function as expected.”
Marketing and Advertising Implications
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has fundamentally reshaped the marketing landscape for mobile applications. The shift from pervasive tracking to user-centric consent significantly impacts how advertisers reach and engage their target audiences. This necessitates a re-evaluation of strategies and a focus on alternative methods of user engagement and data collection.
Impact on Marketing Strategies
ATT has forced a re-evaluation of marketing strategies. The move away from automatic tracking necessitates a more nuanced approach to targeting and user engagement. Marketers must now rely on user consent and alternative data sources to understand user behavior and preferences. This requires careful consideration of user privacy, leading to a more ethical and transparent marketing environment.
Ad Revenue Models and Impact
Different ad revenue models react differently to the limitations imposed by ATT. The shift to user-controlled data collection fundamentally changes how app developers generate revenue from advertising.
| Ad Revenue Model | Impact of ATT |
|---|---|
| Interstitial Ads | Revenue may decrease if users opt out of tracking. |
| In-App Banner Ads | Revenue may decrease if users opt out of tracking, impacting visibility and click-through rates. |
| Rewarded Video Ads | Revenue may decrease if user engagement is limited by opt-outs. |
| Cost-Per-Install (CPI) | Increased reliance on alternative metrics like app store reviews, ratings, and user engagement data, which may require significant investment in alternative marketing approaches. |
| Cost-Per-Click (CPC) | Effectiveness is dependent on the quality of the audience targeting and alternative methods of user acquisition, which may need to be more refined and targeted. |
Advertiser Adaptations to ATT Restrictions
Advertisers are adapting to the restrictions imposed by ATT by focusing on more user-centric approaches. This involves understanding user preferences and motivations to engage in meaningful interactions without relying on pervasive tracking. Sophisticated targeting methods that leverage data from alternative sources, such as app usage patterns, user demographics, and user-provided data, are becoming crucial. Furthermore, clear transparency about how data is collected and used is paramount to build trust and user engagement.
Strategies to Reach Target Audiences Without Tracking
Several strategies can be employed to reach target audiences without relying on tracking. This involves leveraging alternative data sources, focusing on user experience, and prioritizing user privacy.
- Contextual Targeting: This involves using contextual clues within the app to target users based on their activity or the content they engage with. For example, if a user is actively playing a game, advertisements for related items or services can be displayed.
- Behavioral Targeting (with user consent): This approach relies on the user’s explicit permission to gather and analyze data about their behavior within the app to provide tailored advertisements. The focus is on respecting user choices.
- Audience Segmentation: This approach involves dividing the target audience into smaller, more specific segments based on their characteristics, preferences, or behaviors. This allows for more precise targeting.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborating with influencers who align with the target audience can be an effective method to reach potential users.
Effectiveness of Marketing Approaches Pre- and Post-ATT
The effectiveness of marketing approaches has significantly shifted post-ATT. Pre-ATT, many strategies relied heavily on extensive user tracking. Now, strategies that prioritize user consent, data transparency, and contextual targeting have emerged as crucial. Effectiveness will depend on the quality of data used and the level of user engagement with the advertisements.
Alternatives to Traditional Tracking
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has significantly altered the landscape of mobile app development. Developers must now find alternative methods to gather user insights and maintain effective app functionalities without relying on intrusive tracking practices. This necessitates a shift in approach, focusing on user privacy and data collection methods that respect user choices.This section explores various alternatives to traditional tracking techniques, encompassing data collection strategies, user feedback mechanisms, segmentation techniques, and data analysis approaches.
These methods enable a robust understanding of user behavior and preferences without compromising user privacy.
Data Collection Alternatives
Traditional tracking methods, often relying on third-party cookies and identifiers, are now less effective. Instead, developers can utilize alternative data sources and approaches. Direct user input through surveys and feedback forms, coupled with aggregated app usage data, can provide valuable insights without compromising user privacy.
- In-App Surveys and Feedback Mechanisms: Directly collecting user feedback through in-app surveys, polls, and feedback forms provides valuable insights into user experiences and preferences. These methods are particularly useful for understanding specific features or functionalities within the app.
- Aggregated App Usage Data: Analyzing app usage patterns, such as feature usage frequency, session duration, and specific user actions, provides a comprehensive view of user behavior without personally identifiable information. This can be done using analytics tools built into the platform or by leveraging in-app events.
- User-Provided Data Points: Collecting specific, non-sensitive user inputs, such as preferred language or location settings (with user consent), can inform app personalization without relying on broad tracking. For instance, allowing users to choose their preferred currency can tailor the app experience without intrusive tracking.
User Feedback Collection Strategies
Effective user feedback collection is crucial for app improvement and user satisfaction. Structured feedback mechanisms are essential for gathering insights that guide app development and maintenance.
- In-App Feedback Forms: Implementing in-app forms that allow users to provide feedback on specific features, functionalities, or user experience aspects is a direct and efficient method for gathering valuable insights.
- Dedicated Feedback Channels: Creating separate channels, such as a dedicated feedback email address or a dedicated support forum, enables users to provide specific feedback or report issues.
- A/B Testing: Implementing A/B testing on different versions of the app can gauge user preferences and identify elements that improve engagement. By providing different interfaces or functionalities and measuring user responses, developers can determine the optimal design choices.
User Segmentation Strategies
User segmentation allows for targeted improvements and personalized experiences. Segmentation strategies should focus on meaningful data points and avoid personally identifiable information.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Grouping users based on their app usage patterns, such as frequency of use, feature engagement, and session duration, enables targeted content delivery and personalized recommendations.
- Demographic Segmentation: Using non-sensitive demographic data, like preferred language, device type, or operating system version (with user consent), allows developers to tailor app features and content for specific user groups.
Data Analysis and Reporting without Tracking
Data analysis is crucial for understanding user behavior and improving app performance. Effective data analysis techniques can be implemented without compromising user privacy.
- Event-Based Analysis: Analyzing user events within the app, such as button clicks, feature usage, and in-app purchases, allows for a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and app performance.
- Reporting Tools: Leveraging in-app or third-party analytics tools designed for privacy-respecting data analysis is crucial for gathering and visualizing insights without tracking.
- Aggregate Metrics: Focusing on aggregated metrics, such as user engagement rates and app usage trends, offers valuable insights into app performance without revealing individual user data.
Case Studies of ATT Implementation
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has significantly altered the mobile app landscape. Understanding how different apps have navigated these changes provides valuable insights for developers. Analyzing successful implementations, alongside the challenges faced, offers crucial learnings for future strategies.
Examples of Successful ATT Implementations
Various apps have successfully adapted to ATT, demonstrating diverse approaches to maintaining user engagement and revenue. These implementations range from those emphasizing user privacy and transparency to those focusing on alternative tracking methods.
- E-commerce apps often leverage in-app purchases and personalized recommendations to maintain user engagement, even without third-party tracking. They might focus on providing personalized content based on past browsing history, and reward programs. A key strategy is to demonstrate value to the user. For instance, a clothing retailer could highlight exclusive discounts for registered users.
- Social media apps have prioritized transparency and user control. They often present clear explanations of how they use data, including the opt-out options for tracking. Emphasis on providing value through user-generated content and engaging features is critical. For example, a social media app might highlight the ability to connect with friends and family without relying on targeted advertising.
- Productivity apps typically focus on delivering a streamlined user experience. By avoiding intrusive tracking, these apps prioritize a clean and efficient interface. User-feedback mechanisms are often implemented to understand user preferences. For instance, a calendar app might highlight features like automatic reminders and scheduling tools, instead of relying on targeted promotions.
Comparative Analysis of Different Approaches
A comparative analysis of different app approaches can offer valuable insights. The table below highlights key aspects of various ATT implementations.
| App Category | Approach to ATT | Impact on User Engagement | Impact on Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | Personalized recommendations, in-app purchases, loyalty programs | Positive; users appreciate personalized experiences | Positive; increased sales and repeat purchases |
| Social Media | Transparency, user control, community features | Positive; users feel valued and empowered | Positive; engagement leads to higher ad revenue |
| Productivity | Streamlined user experience, feature-rich interface | Positive; users appreciate a clean experience | Positive; users may be less receptive to in-app purchases, revenue model needs adaptation |
Impact on User Engagement and Revenue
The impact of ATT implementations varies significantly depending on the app’s core functionality and revenue model. E-commerce apps often experience positive user engagement through personalized experiences. Social media apps might see a shift in ad revenue, but community features can offset some loss. Productivity apps may experience a shift in the revenue model as they move away from in-app purchases and towards subscriptions or premium features.
Learnings from the Case Studies
The case studies highlight several key learnings for app developers:
- User-centric design is paramount; apps should prioritize user needs and preferences. Offering value directly to the user is key.
- Transparency is essential; clear communication about data usage fosters trust.
- Adaptability is crucial; developers must be prepared to adjust their strategies in response to user preferences and regulatory changes.
- Alternative tracking methods are vital; understanding and implementing these methods can help maintain user engagement and revenue.
Informing Future App Development
These case studies provide a roadmap for app developers looking to implement ATT successfully. Understanding the specific strategies used by successful apps, and the impact on key metrics, can help inform decisions about future development and adaptation.
Future Trends and Implications of ATT
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) has significantly altered the mobile app landscape, forcing developers to adapt their strategies. The evolving user expectations regarding privacy and the potential for future adjustments to ATT regulations demand careful consideration. This section examines potential future changes, forecasts in mobile app development, and emerging technologies shaping the future of data privacy and tracking.
Potential Future Changes to ATT
ATT’s impact on mobile advertising and app monetization is still being assessed. Future adjustments might include refining the opt-out mechanisms to enhance user control. These adjustments could involve more granular options for specific data types or tracking purposes, allowing users to selectively opt out of certain tracking practices while permitting others. Further refinements could also involve mandatory opt-in mechanisms for specific data collection types, mirroring approaches in other regions.
Predictions for the Future of Mobile App Development
Mobile app developers will likely prioritize user privacy by adopting alternative data collection methods. This could involve employing privacy-preserving technologies like federated learning and differential privacy. Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on user-centric design, with a focus on value exchange. Apps that offer clear value propositions and transparent data practices will likely succeed. Examples include apps offering valuable services in exchange for limited data collection, like personalized recommendations based on aggregated, anonymized data.
Emerging Technologies Related to Data Privacy and Tracking
The realm of data privacy and tracking is rapidly evolving. Privacy-preserving technologies like federated learning and differential privacy are gaining traction. Federated learning allows models to be trained on decentralized data without transferring it, preserving user privacy. Differential privacy adds random noise to data, making it harder to identify individual users while still providing useful insights. These techniques are expected to become more integrated into app development processes.
Evolution of User Expectations Regarding Privacy
Users are increasingly aware of data privacy issues and expect greater transparency from apps. They anticipate clear explanations of how their data is used and mechanisms to control data collection. This trend will likely continue, potentially leading to more stringent user expectations in the future. Examples include increased demand for granular control over data sharing and heightened scrutiny of data usage practices.
Role of Transparency in the App Ecosystem
Transparency is becoming a crucial factor in the app ecosystem. Clear data usage policies and opt-out options are critical for building trust and fostering positive user experiences. Users will likely demand greater detail in app privacy policies, leading to more specific disclosures of data collection practices. This approach promotes ethical development and encourages a shift toward a more user-centric app ecosystem.
Comparison of ATT with other Data Privacy Initiatives
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) is a significant development in mobile data privacy, but it’s not an isolated event. It sits within a broader landscape of data privacy regulations and initiatives worldwide. Understanding its relationship with other efforts provides a clearer picture of its impact and future trajectory.ATT, while focused on mobile apps, shares some common ground with other data privacy initiatives, but also possesses unique characteristics.
These similarities and differences highlight the evolving global conversation about user data control and the rights of individuals.
Comparison with Other Data Privacy Regulations
ATT’s primary focus is on user consent for app tracking on iOS devices. This contrasts with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which has a broader scope, encompassing various data processing activities and not just mobile apps. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US, another prominent example, focuses on consumer rights regarding their personal information.
ATT, while addressing tracking, does not address the broader data processing practices covered by GDPR or CCPA. This highlights the varying approaches and granularities of these regulations.
Similarities and Differences, App tracking transparency
Several similarities exist between ATT and other data privacy initiatives. They all aim to empower users with more control over their personal data. Furthermore, they all acknowledge the increasing importance of user consent and transparency in data handling practices. However, the specific mechanisms, scope, and enforcement vary significantly. For example, while all these initiatives seek user control, the specific technologies used to achieve this (like opt-in mechanisms) may differ.
Key Features of Data Privacy Initiatives
| Initiative | Scope | Focus | Enforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| App Tracking Transparency (ATT) | Mobile app tracking on iOS | User consent for tracking | Apple’s App Store guidelines |
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Data processing activities across Europe | User rights over personal data | EU data protection authorities |
| California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) | Consumer rights regarding personal information in California | Consumer control over personal data | California Attorney General |
The table illustrates the different focuses and scopes of these regulations. ATT is limited to the mobile app context, while GDPR and CCPA have broader implications.
Global Impact and Influence
ATT has significantly influenced global data privacy discussions, pushing the conversation toward mobile-specific solutions and highlighting the need for tailored approaches. Its emphasis on user control has spurred similar discussions and actions in other regions. The implications of ATT extend beyond just mobile app developers, influencing how businesses think about user data globally.ATT’s impact is evident in the rising awareness of data privacy issues across the globe.
App tracking transparency is a pretty important issue these days, but sometimes a more immediate problem arises like a phone that won’t turn on. If you’re facing a “phone won’t turn on fix,” checking out this resource on Phone won’t turn on fix might help. Ultimately, though, robust app tracking transparency measures are crucial for user privacy and control.
For example, other countries are now exploring their own mobile app tracking regulations, demonstrating the ripple effect of ATT’s implementation. This has created a global momentum towards user empowerment and greater transparency in data handling.
Potential Issues and Mitigation Strategies: App Tracking Transparency
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) presents both opportunities and challenges for app developers and users. Navigating the potential issues requires a proactive approach, focusing on transparent communication and thoughtful design. Addressing concerns promptly and effectively can foster trust and maintain a positive user experience.Understanding the potential conflicts between user privacy preferences and app functionality is crucial. Developing strategies to mitigate these conflicts and maintain a robust user experience is essential.
This includes proactive communication, flexible design, and comprehensive documentation for developers.
Potential Issues with ATT
Implementing ATT necessitates careful consideration of potential issues. These can range from decreased ad revenue to user confusion. Failure to address these issues can lead to a decline in user engagement and ultimately, app adoption. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to ensure smooth transition.
- Reduced Ad Revenue: ATT’s limitations on data collection for ad personalization can directly impact ad revenue for apps that rely heavily on targeted advertising. This is especially true for apps that offer free services and monetize through advertising. Developers need to adapt monetization strategies to compensate for the reduced ad revenue.
- User Confusion and Frustration: Users may struggle to understand the implications of ATT prompts and their choices. Complex or confusing interfaces can lead to user frustration and a decline in app usage. Transparent and straightforward explanations are key to alleviating this issue.
- App Functionality Limitations: Some apps heavily rely on data collection for features like personalized recommendations or tailored content. ATT limitations can restrict the functionality of these features. Developers must adapt their app designs to provide alternative methods for delivering similar functionality.
- Increased Development Costs: Adjusting apps to comply with ATT’s requirements might entail increased development costs. This could include creating alternative data collection mechanisms or redesigning user interfaces. Planning and budgeting for these adjustments are vital.
Mitigation Strategies for ATT Issues
Addressing the potential issues requires proactive strategies. Developing robust solutions for these concerns is crucial for maintaining app functionality and user engagement.
- Alternative Monetization Strategies: Diversifying revenue streams can mitigate the impact of reduced ad revenue. This could include in-app purchases, subscriptions, or partnerships with other businesses. The transition to new models requires careful planning and market analysis.
- User-Friendly Interface Design: Creating a user-friendly interface for ATT prompts is critical to reduce user confusion. Clear explanations and visual cues can significantly improve user understanding. Visual aids and detailed explanations can effectively communicate the purpose and importance of data collection.
- Feature Adjustments: Apps can explore alternative methods to deliver functionality impacted by ATT limitations. This could involve using aggregated user data, user-provided inputs, or employing alternative algorithms. Finding alternative solutions that deliver similar value is essential.
- Cost-Effective Implementation: Developing cost-effective strategies for ATT implementation is crucial. This involves careful planning, strategic resource allocation, and prioritizing essential changes. A phased approach to implementing changes can help manage costs effectively.
Transparent User Interfaces for ATT
Designing a transparent interface for ATT is essential for maintaining user trust. Clearly communicating the app’s data collection practices and user choices is vital.
- Clear and Concise Language: Use simple and concise language to explain the purpose of data collection and how user choices impact app functionality. Avoid technical jargon and provide examples.
- Visual Aids: Employ visual aids, such as icons or diagrams, to enhance the understanding of ATT prompts. Visual cues can improve clarity and reduce ambiguity.
- User Control: Provide users with clear control over their data choices. Users should be able to easily review and modify their preferences regarding data collection. Clear mechanisms for users to adjust settings should be implemented.
- Detailed Explanations: Provide detailed explanations for why the app collects certain data. This transparency builds trust and ensures users understand the value of data collection.
Resources for Addressing ATT Concerns
A comprehensive resource library for developers is crucial. This should cover best practices and common concerns regarding ATT implementation.
- Apple’s Developer Documentation: Apple’s official documentation is a valuable resource for understanding ATT and its implementation.
- Developer Forums and Communities: Participating in developer forums and communities allows developers to learn from peers and address specific concerns.
- Industry Blogs and Publications: Following industry blogs and publications provides updates on best practices, case studies, and emerging trends.
- Third-Party Tools and Services: Utilizing third-party tools and services designed for ATT compliance can ease the implementation process. These services can often assist in understanding specific data requirements.
Final Summary
In conclusion, App tracking transparency represents a substantial shift in mobile app development, demanding transparency and user-centric design. Developers must adapt their strategies to respect user privacy, while users gain more control over their data. The future of mobile apps hinges on this evolving relationship between user privacy and app functionality.
FAQ
What is the purpose of App Tracking Transparency?
App Tracking Transparency (ATT) aims to give users more control over how their data is collected and used by apps. It provides a clear framework for permission requests and transparency in data handling.
How does ATT affect marketing strategies?
ATT necessitates adjustments to marketing strategies. Developers need to explore alternative ways to target audiences without relying on tracking user data.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with ATT?
Non-compliance with ATT can result in user backlash, reduced app downloads, and potential legal repercussions. Specific penalties may vary depending on the region and the severity of the violation.
What are some alternative methods for collecting user data without tracking?
Alternative methods include user feedback surveys, in-app analytics (with explicit user consent), and user segmentation based on explicit user preferences.