Decentralized internet platforms are emerging as a compelling alternative to traditional centralized models. These platforms offer a unique approach to online interaction, promising greater user control, enhanced security, and censorship resistance. From decentralized social media to secure storage, the potential applications are vast and varied.
This exploration dives deep into the world of decentralized internet platforms, examining their underlying technologies, user experiences, economic models, and the crucial security considerations involved. We will analyze the challenges and opportunities in integrating these innovative platforms into the existing internet landscape.
Defining Decentralized Internet Platforms
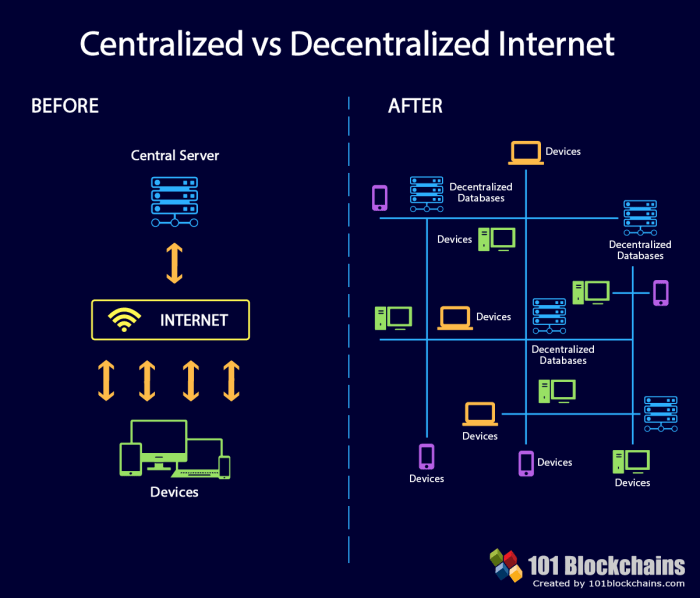
Decentralized internet platforms are emerging as a significant alternative to traditional, centralized online services. These platforms aim to empower users by shifting control and ownership from a central authority to a distributed network. This shift promises enhanced security, resilience, and user autonomy. The core principles underpinning these platforms differ drastically from their centralized counterparts.Decentralized internet platforms operate on a distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain.
This distributed nature, coupled with cryptographic security, forms the foundation for their resilience and resistance to censorship. Unlike centralized platforms, which often rely on a single point of failure, decentralized platforms are less vulnerable to attacks and outages.
Core Principles of Decentralization
Decentralized platforms rely on distributed networks, ensuring no single entity controls the system. This contrasts sharply with centralized platforms, where a central authority dictates policies, controls data, and manages access. Cryptographic security, often implemented using blockchain technology, plays a critical role in ensuring data integrity and authenticity. Transparency is another cornerstone, enabling users to understand how the platform operates and the implications of their interactions.
Types of Decentralized Internet Platforms
Various types of decentralized platforms cater to diverse needs. Decentralized social media platforms, for instance, empower users to control their data and interactions. These platforms often utilize blockchain technology to facilitate secure and transparent communication. Decentralized storage platforms offer a secure and redundant way to store data, eliminating reliance on single servers. Decentralized marketplaces provide a peer-to-peer trading environment, often with reduced transaction fees and greater control for participants.
Examples of Decentralized Internet Platforms
Several decentralized internet platforms are already operational, showcasing the viability of this model. Examples include decentralized social media platforms like Mastodon, which prioritize user privacy and freedom of expression. Decentralized storage solutions like Filecoin and IPFS offer secure and scalable data storage alternatives. Decentralized marketplaces like OpenBazaar enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries.
Comparison of Decentralized and Centralized Platforms
| Criteria | Decentralized Platforms | Centralized Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Enhanced security due to distributed nature and cryptographic measures; less vulnerable to single points of failure. | Security often relies on the security of a central entity, potentially exposing users to vulnerabilities and risks of centralized control. |
| Censorship Resistance | Less susceptible to censorship due to the distributed network and lack of central control. | Censorship is often possible by the central authority. |
| User Control | Users have greater control over their data and interactions. | Users have limited control over their data and are subject to the platform’s policies. |
| Transaction Fees | Potentially lower transaction fees due to the absence of intermediaries. | Transaction fees are often determined by the platform and intermediaries. |
| Scalability | Scalability can be a challenge depending on the specific platform and technology. | Scalability can be managed more easily due to central control and resources. |
Technical Architecture of Decentralized Platforms

Decentralized internet platforms leverage innovative technologies to operate independently of central authorities. This approach, while promising, necessitates robust technical architectures that support security, scalability, and resilience. These platforms rely on a combination of distributed ledger technologies, cryptographic techniques, and consensus mechanisms to achieve their decentralized goals.The core of these platforms lies in their distributed nature, which fundamentally alters how data and transactions are managed.
This contrasts sharply with traditional centralized systems, which often rely on single points of failure. This distributed model necessitates the use of sophisticated underlying technologies to maintain integrity, security, and efficiency.
Underlying Technologies
Decentralized platforms utilize various technologies to facilitate secure and transparent operations. Blockchain technology, a cornerstone of many decentralized platforms, records transactions in a shared, immutable ledger. Cryptocurrencies, often integral to these platforms, enable secure and verifiable transactions between users. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a broader concept encompassing various approaches to distributed data management, providing the framework for managing transactions and data in a shared and transparent manner.
Decentralized internet platforms are gaining traction, offering a more secure and user-controlled online experience. However, navigating the tech landscape can be tricky, especially when considering a new gadget like a smartwatch. For a comprehensive guide on choosing the right smartwatch, check out this helpful resource: Smartwatch buying guide. Ultimately, these platforms and their associated tech, like smartwatches, are part of a broader movement toward more democratic and user-centric digital spaces.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are crucial for decentralized platforms. They ensure that all participants agree on the state of the system. Different mechanisms exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Proof-of-work (PoW), a mechanism used in Bitcoin, involves computational effort to validate transactions. Proof-of-stake (PoS), a more energy-efficient alternative, leverages the stake held by participants to validate transactions.
Other mechanisms, such as delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), delegate validation to a smaller group of trusted nodes.
Decentralized internet platforms offer an intriguing alternative to centralized ones, potentially enhancing user privacy and security. However, the distributed nature of these systems also presents new challenges, particularly in terms of phishing and malware prevention. Robust security measures are crucial to safeguarding users on these platforms, much like traditional systems need strong phishing and malware prevention strategies.
Ultimately, the future of decentralized internet platforms hinges on addressing these issues effectively.
Technical Infrastructure
The technical infrastructure supporting decentralized platforms involves numerous components. These include node networks, which are distributed points of access and validation for the platform. Data storage solutions are also crucial for maintaining the platform’s integrity and accessibility. Furthermore, communication protocols and APIs allow for seamless interaction between users and the platform. These protocols and APIs must be designed for efficiency and resilience, considering the distributed nature of the platform.
Security Measures
Security is paramount in decentralized platforms. Cryptography plays a critical role in securing data and transactions. Encryption techniques ensure that sensitive information remains confidential. Digital signatures verify the authenticity of transactions and prevent unauthorized modifications. Furthermore, robust access control mechanisms regulate user interaction with the platform, mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access.
Technical Components and Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Blockchain | Stores and verifies transactions in a shared, immutable ledger. |
| Cryptocurrencies | Enable secure and verifiable transactions between users. |
| Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) | Provides a framework for managing transactions and data in a shared and transparent manner. |
| Node Networks | Distributed points of access and validation for the platform. |
| Data Storage | Maintains the platform’s integrity and accessibility. |
| Communication Protocols and APIs | Enable seamless interaction between users and the platform. |
User Experience and Interface
Decentralized internet platforms, while promising enhanced security and user control, require careful consideration of user experience (UX) and interface design. A positive and intuitive interface is crucial for widespread adoption. This section delves into the crucial aspects of UX design for such platforms, focusing on privacy, user control, and effective onboarding.
User Privacy and Control
Decentralized platforms offer users a significant degree of control over their data and online interactions. Users can maintain ownership of their digital assets, identities, and interactions, mitigating potential data breaches and privacy violations often associated with centralized platforms. This enhanced control translates to greater user agency and a sense of empowerment.
User-Friendly Interfaces on Existing Decentralized Platforms
Several decentralized platforms are demonstrating user-friendly interfaces. For instance, some decentralized social media platforms employ intuitive feed structures and personalized content recommendations. Similarly, decentralized file storage platforms often feature drag-and-drop functionalities and clear file management tools. These examples showcase that decentralized platforms can be accessible and user-friendly.
Onboarding New Users
Effective onboarding is vital for successful user adoption. A well-structured onboarding process should clearly communicate the platform’s unique features and benefits, guiding new users through the initial steps. This often involves providing clear explanations of how to interact with the platform, access functionalities, and manage their accounts. Interactive tutorials and step-by-step guides are often incorporated to facilitate the onboarding process.
User Interface Elements and Functionalities
A well-designed user interface (UI) is essential for a positive user experience. A clear structure and intuitive navigation are key. The following table illustrates various UI elements and their functionalities in a decentralized application.
| Element | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Dashboard | Provides an overview of user accounts, transactions, and other relevant information. |
| Profile Settings | Enables users to manage their personal information, security settings, and preferences. |
| Transaction History | Displays a chronological record of user transactions, including details of sender, recipient, amount, and date. |
| Notification Center | Provides alerts and updates about platform activities, such as new messages, comments, or interactions. |
| Search Bar | Allows users to locate specific content, users, or information within the platform. |
| Navigation Menu | Facilitates easy access to different sections and functionalities of the platform. |
| Buttons (e.g., “Post,” “Share,” “Send”) | Initiate specific actions, such as creating posts, sharing content, or sending messages. |
Security and Privacy Considerations: Decentralized Internet Platforms
Decentralized internet platforms offer a compelling alternative to centralized models, but they also present unique security and privacy challenges. Robust security measures are crucial to fostering trust and adoption. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate countermeasures is paramount for the success of these platforms.
Security Measures on Decentralized Platforms, Decentralized internet platforms
Decentralized platforms leverage various security measures to protect user data and transactions. Cryptographic techniques, like encryption and hashing, play a vital role in securing data transmission and storage. These methods ensure that only authorized parties can access sensitive information. Furthermore, consensus mechanisms, which are integral to blockchain technology, verify transactions and maintain data integrity across the network.
This distributed nature of validation makes it exceptionally challenging for malicious actors to manipulate the system.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Decentralized platforms, while offering enhanced security through decentralization, are not immune to risks. Smart contract vulnerabilities, if not meticulously audited, can lead to significant financial losses and compromise user assets. Node compromise, a scenario where a key node on the network is compromised, could potentially disrupt the platform’s functionality or lead to data breaches. Furthermore, the lack of central control can pose difficulties in addressing disputes and enforcing regulations.
The sheer complexity of these systems can lead to vulnerabilities that are difficult to anticipate or identify in the initial design.
Comparison of Security Protocols
Centralized systems often rely on a single point of failure, making them more susceptible to breaches and outages. Decentralized systems, in contrast, distribute the responsibility for security across multiple nodes, enhancing resilience against attacks. Centralized systems typically employ traditional security protocols like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, while decentralized systems often incorporate cryptographic techniques and blockchain-specific security measures.
Examples of Successful Security Strategies
Numerous decentralized platforms have implemented innovative security strategies. For example, platforms using zero-knowledge proofs can verify transactions without revealing sensitive information. Auditing smart contracts before deployment is a common practice to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Furthermore, platforms employing multi-signature wallets enhance the security of user assets by requiring multiple parties to authorize transactions.
Table Comparing Security Features Across Platforms
| Platform | Consensus Mechanism | Smart Contract Auditing | Data Encryption | User Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform A | Proof-of-Stake | Manual, third-party audits | AES-256 | Multi-factor authentication |
| Platform B | Proof-of-Work | Automated, on-chain audits | Elliptic Curve Cryptography | Decentralized identity solutions |
| Platform C | Delegated Proof-of-Stake | Community-based security audits | Hybrid encryption | Biometric authentication |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Actual security features and implementations can vary significantly across platforms. Each platform will have its own specific strengths and weaknesses.
Last Recap
In conclusion, decentralized internet platforms represent a significant shift in how we interact online. While challenges remain regarding scalability and integration, the potential for enhanced user control, security, and censorship resistance is undeniable. The future of the internet may well be decentralized, and this analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the factors shaping its evolution.
FAQ Section
What are the key differences between decentralized and centralized platforms?
Centralized platforms rely on a single entity to control the data and infrastructure, while decentralized platforms distribute control among multiple users or nodes. This distribution often improves security and resilience but can impact scalability.
What are some common use cases for decentralized internet platforms?
Decentralized social media, secure file storage, and peer-to-peer marketplaces are among the burgeoning use cases.
What are the potential risks of decentralized internet platforms?
Potential risks include scalability issues, complexity of integration with existing systems, and security vulnerabilities inherent in any new technology.
How do decentralized platforms address censorship concerns?
By distributing control among numerous users, decentralized platforms can potentially reduce the ability of a single entity to censor content.





